News
Guidance on Red & Black Solar Cable Selection

Solar power systems rely on efficient wiring to ensure maximum energy transfer from photovoltaic (PV) panels to inverters, batteries, and the grid. Among the most critical components are red and black solar cables, which serve as the primary conductors for DC power transmission.
Choosing the right solar cables is essential for system efficiency, safety, and longevity. This guide will cover:
- The importance of red and black solar cables
- Key specifications to consider
- Differences between standard and PV-specific cables
- Installation best practices
Why Red & Black Solar Cables Matter
Solar cables are color-coded for easy identification:
- Red cables typically carry the positive (+) DC current.
- Black cables carry the negative (-) DC current.
Using the correct colors ensures proper polarity, reducing the risk of short circuits and improving maintenance efficiency.
Key Benefits of High-Quality Solar Cables
- UV Resistance – Withstands prolonged sun exposure.
- Weatherproof – Resists moisture, extreme temperatures, and abrasion.
- High Conductivity – Minimizes power loss over long distances.
- Fire Resistance – Prevents overheating and fire hazards.
Technical Specifications for Solar Cable Selection
When selecting solar cables, consider these critical factors:
1. Cable Gauge (AWG)
- 10 AWG to 12 AWG – Common for residential solar systems.
- 8 AWG to 4 AWG – Used in commercial or high-current applications.
Thicker cables (lower AWG) reduce voltage drop over long distances.
2. Voltage Rating
- 600V to 2000V – Standard for solar applications.
- Ensure compatibility with your system’s max voltage.
3. Temperature Range
- -40°C to 90°C – Ideal for outdoor use.
- Some cables can handle up to 120°C for extreme conditions.
4. Insulation Material
- Cross-Linked Polyethylene (XLPE) – Best for durability.
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) – Cheaper but less UV-resistant.
5. Certifications
Look for:
- TÜV Rheinland (PV-specific certification)
- UL 4703 (US standard for PV wire)
- IEC 62930 (International solar cable standard)
Solar Cable vs. Standard Electrical Wire
Many people mistakenly use standard electrical wires for solar installations, leading to inefficiencies and safety risks.
| Feature | Solar Cable | Standard Electrical Wire |
|---|---|---|
| UV Resistance | Excellent | Poor |
| Temperature Range | Wider (-40°C to 120°C) | Limited (0°C to 60°C) |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible for routing | Stiffer |
| Fire Safety | Flame-retardant | May not meet PV standards |
Always use PV-rated cables for solar installations.
Installation Best Practices
Proper installation ensures efficiency and safety:
1. Correct Sizing
Use a voltage drop calculator to determine the right cable gauge based on:
- System voltage
- Current (Amps)
- Distance between panels and inverter
2. Secure Connections
- Use MC4 connectors (industry standard for solar).
- Ensure waterproof seals to prevent corrosion.
3. Avoid Sharp Bends
- Maintain a minimum bend radius (usually 5x cable diameter).
- Prevents insulation damage.
4. Proper Grounding
- Prevents electrical surges.
- Follow NEC (National Electrical Code) or IEC standards.
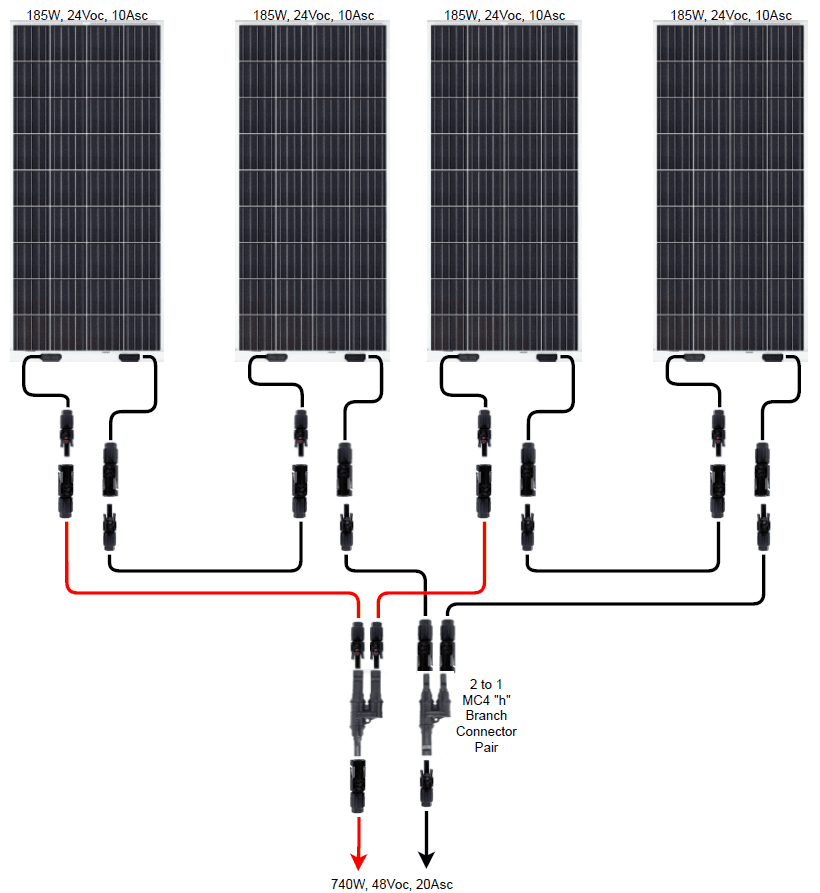
Correct solar cable routing and connections.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solar Cables
Selecting the correct red and black solar cables is crucial for system efficiency, safety, and compliance. Always prioritize:
- PV-specific certifications
- Proper gauge sizing
- High UV and temperature resistance
- Professional installation techniques
By following this guide, you ensure a long-lasting, high-performance solar power system.
FAQs
Q: Can I use regular electrical wire for solar panels?
A: No, standard wires lack UV and temperature resistance, leading to premature failure.
Q: What’s the difference between 10 AWG and 12 AWG solar cables?
A: 10 AWG handles higher current with less voltage drop over long distances.
Q: Are all red and black cables solar-rated?
A: No, always check for PV wire markings (e.g., PV1-F, TÜV certified).
Q: How often should solar cables be inspected?
A: At least once a year for wear, corrosion, or damage.